| 3.5. Configuration using XML | ||
|---|---|---|
 | Chapter 3. Configuration |  |
An XML file is a text file (i.e. contains human-readable characters only) with formally defined structure and content. An XML file starts with the line :-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
This defines the version of XML that the file complies with and the character encoding in use. The UTF-8 character coding is used everywhere by the FireBrick.
The XML file contains one or more elements, which may be nested into a hiearchy.
In XML, the configuration objects are represented by elements, so the terms object and element are used interchangeably in this manual.
Each element consists of some optional content, bounded by two tags - a start tag AND an end tag.
A start tag consists of the following sequence of characters:-
An end tag consists of the following sequence of characters:-
If an element needs no content, it can be represented with a more compact self closing tag. A self closing tag is the same as a start tag but ends with /> and then has no content or end tag.
Since the <, > and " characters have special meaning, there
are special ('escape') character sequences starting with the ampersand character that are used to represent these characters. They are :-
Note that since the ampersand character has special meaning, it too has an escape character sequence.
Attributes are written in the form : name="value" or name='value'. Multiple attributes are
separated by white-space (spaces and line breaks).
Generally, the content of an element can be other child elements or text. However, the FB6000 doesn't use text content in elements - all configuration data is specified via attributes. Therefore you will see that elements only contain one or more child elements, or no content at all. Whilst there is generally not any text between the tags, white space is normally used to make the layout clear.
At the top level, an XML file normally only has one element (the root element), which contains the entire element hierarchy.
In the FB6000 the root element is <config>, and it contains 'top-level' configuration elements that cover major areas
of the configuration, such as overall system settings, interface definitions, firewall rule sets etc.
In addition to this User Manual, there is reference material is available that documents the XML elements - refer to Section 3.2.1.
The XML representation of the configuration can be viewed and edited (in text form) via the web interface by clicking on "XML View" and "XML Edit" respectively under the main-menu "Config" item. Viewing the configuration is, as you might expect, 'read-only', and so is 'safe' in as much as you can't accidentally change the configuration.
An example of a simple, but complete XML configuration is shown below, with annotations pointing out the main elements
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config xmlns="http://firebrick.ltd.uk/xml/fb2700/"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://firebrick.ltd.uk/xml/fb2700/ ...
timestamp="2011-10-14T12:24:07Z"
patch="8882">
<system name="gateway" 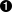 contact="Peter Smith"
location="The Basement"
log-panic="fb-support">
</system>
<user name="peter"
contact="Peter Smith"
location="The Basement"
log-panic="fb-support">
</system>
<user name="peter" 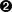 full-name="Peter Smith"
password="FB105#4D42454D26F8BF5480F07DFA1E41AE47410154F6"
timeout="PT3H20M"
config="full"
level="DEBUG"/>
<log name="default"/>
full-name="Peter Smith"
password="FB105#4D42454D26F8BF5480F07DFA1E41AE47410154F6"
timeout="PT3H20M"
config="full"
level="DEBUG"/>
<log name="default"/>  <log name="fb-support">
<email to="crashlog@firebrick.ltd.uk"
comment="Crash logs emailed to FireBrick Support"/>
</log>
<services>
<log name="fb-support">
<email to="crashlog@firebrick.ltd.uk"
comment="Crash logs emailed to FireBrick Support"/>
</log>
<services>  <ntp timeserver="pool.ntp.org"/>
<telnet log="default"/>
<http />
<dns domain="watchfront.co.uk"
resolvers="81.187.42.42 81.187.96.96"/>
</services>
<port name="WAN"
<ntp timeserver="pool.ntp.org"/>
<telnet log="default"/>
<http />
<dns domain="watchfront.co.uk"
resolvers="81.187.42.42 81.187.96.96"/>
</services>
<port name="WAN"  ports="1"/>
<port name="LAN"
ports="2"/>
<interface name="WAN"
port="WAN">
<subnet name="ADSL"
ip="81.187.106.73/30"/>
</interface>
<interface name="LAN"
ports="1"/>
<port name="LAN"
ports="2"/>
<interface name="WAN"
port="WAN">
<subnet name="ADSL"
ip="81.187.106.73/30"/>
</interface>
<interface name="LAN"  port="LAN">
<subnet name="LAN"
ip="81.187.96.94/28"/>
<dhcp name="LAN"
ip="81.187.96.88-92"
log="default"/>
</interface>
</config>
port="LAN">
<subnet name="LAN"
ip="81.187.96.94/28"/>
<dhcp name="LAN"
ip="81.187.96.88-92"
log="default"/>
</interface>
</config>
sets some general system parameters (see Section 4.2) | |
defines a single user with the highest level of access (DEBUG) (see Section 4.1) | |
defines a log target (see Chapter 5) | |
configures key system services (see Chapter 12) | |
defines physical-port group (see Section 6.1) | |
defines an interface, with one subnet and a DHCP allocation pool (see Chapter 6) |